Characteristic Of A Denial Of Service Attack?
What is a denial-of-service attack?
A deprival-of-service (DoS) attack is a security threat that occurs when an aggressor makes it incommunicable for legitimate users to access computer systems, network, services or other information engineering (IT) resources. Attackers in these types of attacks typically inundation web servers, systems or networks with traffic that overwhelms the victim's resources and makes information technology hard or impossible for anyone else to access them.
Restarting a organization will usually fix an attack that crashes a server, simply flooding attacks are more difficult to recover from. Recovering from a distributed DoS (DDoS) attack in which attack traffic comes from a large number of sources is even more than difficult.
DoS and DDoS attacks often take reward of vulnerabilities in networking protocols and how they handle network traffic. For example, an attacker might overwhelm the service by transmitting many packets to a vulnerable network service from different Cyberspace Protocol (IP) addresses.
How does a DoS attack work?
DoS and DDoS attacks target i or more than of the seven layers of the Open up Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. The most mutual OSI targets include Layer three (network), Layer 4 (transport), Layer 6 (presentation) and Layer 7 (application).
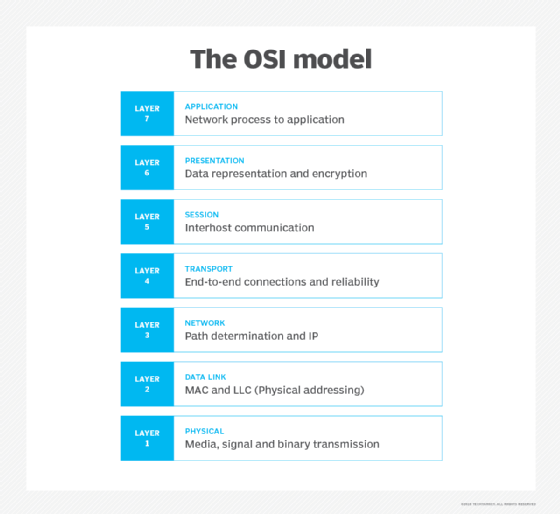
Malicious actors accept different ways of attacking the OSI layers. Using User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets is one common way. UDP speeds transmission transferring data before the receiving party sends its agreement. Another mutual assail method is SYN (synchronization) bundle attacks. In these attacks, packets are sent to all open ports on a server, using spoofed, or fake, IP addresses. UDP and SYN attacks typically target OSI Layers 3 and 4.
Protocol handshakes launched from net of things (IoT) devices are now usually used to launch attacks on Layers half-dozen and 7. These attacks tin be difficult to identify and preempt because IoT devices are everywhere and each is a discrete intelligent client.
Signs of a DoS attack
The United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team, also known as The states-CERT, provides guidelines to determine when a DoS attack may be in progress. According to Usa-CERT, the following may indicate an assail is underway:
- slower or otherwise degraded network functioning that is especially noticeable when trying to access a website or open up files on the network;
- inability to access a website; or
- more spam email than usual.

Preventing a DoS assail
Experts recommend several strategies to defend confronting DoS and DDoS attacks, starting with preparing an incident response programme well in advance.
An enterprise that suspects a DoS attack is underway should contact its internet service provider (Isp) to determine whether boring performance or other indications are from an attack or some other gene. The Isp can reroute the malicious traffic to counter the attack. Information technology can besides apply load balancers to mitigate the severity of the set on.
ISPs as well have products that discover DoS attacks, as do some intrusion detection systems (IDSes), intrusion prevention systems (IPSes) and firewalls. Other strategies include contracting with a backup Internet service provider and using cloud-based anti-DoS measures.
In that location have been instances where attackers have demanded payment from victims to end DoS or DDoS attacks, but financial profit is not usually the motive behind these attacks. In many cases, the attackers wish to harm the business organisation or reputation of the organization or individual targeted in the attack.
Types of DoS attacks
DoS and DDoS attacks have a variety of methods of attack. Common types of deprival-of-service attacks include the post-obit:
- Application layer. These attacks generate fake traffic to internet awarding servers, especially domain name organisation (DNS) servers or Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) servers. Some awarding layer DoS attacks flood the target servers with network data; others target the victim's awarding server or protocol, looking for vulnerabilities.
- Buffer overflow . This type of attack is ane that sends more traffic to a network resources than it was designed to handle.
- DNS amplification . In a DNS DoS attack, the attacker generates DNS requests that appear to have originated from an IP address in the targeted network and sends them to misconfigured DNS servers managed by tertiary parties. The amplification occurs as the intermediate DNS servers respond to the fake DNS requests. The responses from intermediate DNS servers to the requests may contain more information than ordinary DNS responses, which requires more resource to procedure. This can result in legitimate users being denied access to the service.
- Ping of death . These attacks abuse the ping protocol past sending request letters with oversized payloads, causing the target systems to become overwhelmed, to stop responding to legitimate requests for service and to possibly crash the victim's systems.
- State exhaustion. These attacks -- also known as Transmission Control Protocol ( TCP) attacks -- occur when an attacker targets the state tables held in firewalls, routers and other network devices and fills them with attack data. When these devices incorporate stateful inspection of network circuits, attackers may exist able to fill up the country tables past opening more TCP circuits than the victim's system tin handle at one time, preventing legitimate users from accessing the network resource.
- SYN flood . This attack abuses the TCP handshake protocol by which a customer establishes a TCP connection with a server. In a SYN alluvion attack, the assaulter directs a high-volume stream of requests to open TCP connections with the victim server with no intention of completing the circuits. A successful set on can deny legitimate users access to the targeted server.
- Teardrop. These attacks exploit flaws like how older operating systems (OSes) handled fragmented IP packets. The IP specification enables packet fragmentation when the packets are too big to be handled past intermediary routers, and it requires packet fragments to specify fragment offsets. In teardrop attacks, the fragment offsets are ready to overlap each other. Hosts running afflicted OSes are then unable to reassemble the fragments, and the assault tin can crash the arrangement.
- Volumetric. These DoS attacks employ all the bandwidth bachelor to reach network resources. To do this, attackers must straight a high volume of network traffic at the victim'southward systems. Volumetric DoS attacks flood a victim's devices with network packets using UDP or Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). These protocols require relatively piffling overhead to generate big volumes of traffic, while, at the aforementioned time, the victim'south network devices are overwhelmed with network packets, trying to procedure the incoming malicious datagrams.
What is DDoS and how does information technology compare to DoS?
Many high-profile DoS attacks are actually distributed attacks, where the assail traffic comes from multiple set on systems. DoS attacks originating from one source or IP address can be easier to counter considering defenders can cake network traffic from the offending source. Attacks from multiple attacking systems are far more difficult to detect and defend against. It can exist difficult to differentiate legitimate traffic from malicious traffic and filter out malicious packets when they are being sent from IP addresses seemingly located all over the internet.
In a distributed deprival-of-service set on, the attacker may utilize computers or other network-continued devices that have been infected by malware and made role of a botnet. DDoS attacks use command-and-command servers (C&C servers) to control the botnets that are part of the assail. The C&C servers dictate what kind of set on to launch, what types of data to transmit, and what systems or network connectivity resources to target with the attack.
History of deprival-of-service attacks
DoS attacks on net-connected systems have a long history that arguably started with the Robert Morris worm attack in 1988. In that set on, Morris, a graduate pupil at Massuchusetts Plant of Technology (MIT), released a cocky-reproducing slice of malware -- a worm -- that quickly spread through the internet and triggered buffer overflows and DoS attacks on the affected systems.
Those connected to the net at the fourth dimension were mostly inquiry and bookish institutions, but it was estimated that as many as 10% of the 60,000 systems in the U.Due south. were affected. Impairment was estimated to be as high equally $10 million, co-ordinate to the U.S. Full general Bookkeeping Office (GAO), now known as the Government Accountability Function. Prosecuted under the 1986 Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), Morris was sentenced to 400 community service hours and iii years' probation. He was also fined $10,000.
DoS and DDoS attacks have become mutual since then. Some contempo attacks include the following:
- GitHub. On Feb. 28, 2018, GitHub.com was unavailable because of a DDoS attack. GitHub said it was offline for nether 10 minutes. The set on came "across tens of thousands of endpoints … that peaked at 1.35 terabits per second (Tbps) via 126.9 million packets per second," according to GitHub.
- Imperva. On April xxx, 2019, network security vendor Imperva said it recorded a large DDoS attack against one of its clients. The assault peaked at 580 million packets per second merely was mitigated past its DDoS protection software, the company said.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS). In the AWS Shield Threat Landscape Report Q1 2020, the cloud service provider (CSP) said it mitigated ane of the largest DDoS attack it had e'er seen in February 2020. It was 44% larger than anything AWS had encountered. The volume of the assault was ii.3 Tbps and used a blazon of UDP vector known every bit a Connection-less Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (CLDAP) reflection. Amazon said it used its AWS Shield to counter the set on.
This was last updated in Apr 2021
Keep Reading Near denial-of-service set on
- 6 common types of cyber attacks and how to preclude them
- The ultimate guide to cybersecurity planning for businesses
- ten types of security incidents and how to handle them
- Credential stuffing: When DDoS isn't DDoS
- The dark web in 2021: Should enterprises exist worried?
Dig Deeper on Network security
-

SYN flood assail
-

Implement API rate limiting to reduce set on surfaces
-

IP spoofing
-

distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack
Characteristic Of A Denial Of Service Attack?,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/denial-of-service
Posted by: crusedowasobod.blogspot.com




0 Response to "Characteristic Of A Denial Of Service Attack?"
Post a Comment